Uses Of Prepositions Pdf

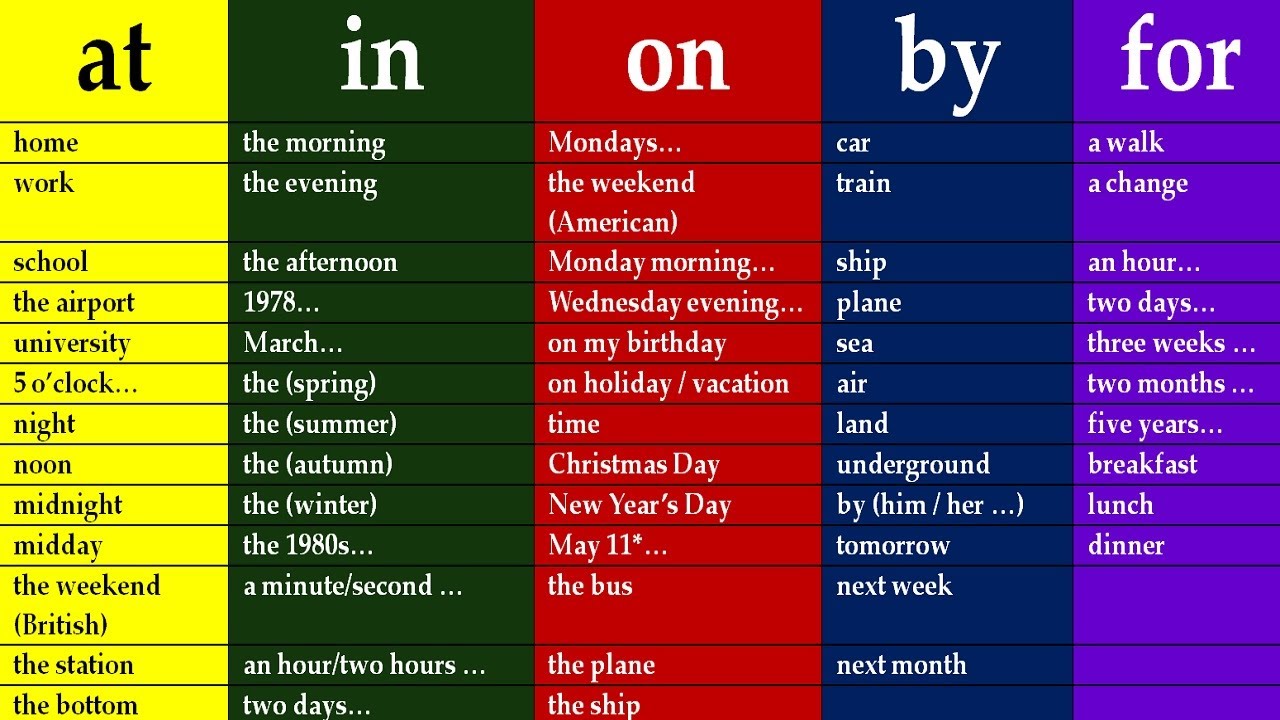
Preposition Chart. How It's Used. Showing Time. At exact times meal times parts of the day age at 3pm at dinner at sundown at age. PREPOSITIONS A preposition is a word that relates a noun or pronoun to another word in a sentence. 'The dog sat under the tree.' About above across after against along among around at before behind below beneath beside between by down during except for from in in front of inside instead of into like near of off on onto on top of out of outside over.
Preposition RulesDid you know there are in the English language? A fun way to remember prepositions is that they are words that tell you everywhere a bunny can run; for example, a bunny can run:.
up. down. near. far.
by. at.
around. close. alwaysWith some of these popular prepositions in mind, let's look at six important rules for prepositions.
Pair Them ProperlyDetermining which preposition to use can be a tricky proposition. It's especially difficult when - expressions in the English language that don't necessarily make sense when taken literally.Idiomatic expressions are expressions you just have to memorize, and when errors are made, they're almost always prepositional errors.
Here are some examples of idioms, along with the correct prepositions:. George would love to attend the party. You're capable of anything you set your mind to. Shelly's been preoccupied with work lately. The teacher is concerned by Janette's consistent tardiness. Employees are prohibited from smoking on company property.Each of the prepositions in bold are the only acceptable prepositions to follow the verbs that precede them. For example, it wouldn't be grammatically correct to say 'love with' or 'capable to.'
Uses Of Prepositions In English Grammar Pdf
For more, enjoy. Watch What Follows ThemPrepositions must always be followed by a. That noun is called the object of the preposition. Note that a can't be the object of a preposition. Let's look at two examples:. The bone was for the dog.This is correct.
The preposition for is followed by the noun 'dog.' . The bone was for walked.This is not correct. The preposition for is followed by a verb 'walked.' A verb can never be the object of a preposition.This rule may seem confusing at first; you may have seen words that look like verbs following the preposition to.
For example:. I like to ski. These boots are for skiing.However, in these examples, 'ski' and 'skiing' are not acting as verbs.In the first example, to ski is. An infinitive occurs when a verb is used as a noun, adjective, or adverb.
Here, to ski is a thing that the person likes doing, not an action they are performing.In the second example, skiing is a. Although a gerund is created out of a verb, it's actually a noun. Here, skiing is a thing that the boots are for. No one in this sentence is performing the act of skiing.
Avoid Using Them at the End of SentencesBecause prepositions must be followed by a noun and have an object, they should rarely be placed at the end of a sentence. For example, it's generally not correct to say:. The table is where I put my books on.However, there are certain circumstances where it is acceptable to. These exceptions exist where the preposition isn't extraneous. In other words, the preposition needs to be there, and if it wasn't, the meaning of the sentence would change.In the above example, the use of the preposition 'on' isn't necessary. We could remove 'on' and the meaning would be the same.
Therefore, the preposition was extraneous or unnecessary. That said, here's an example where it's perfectly acceptable to use a preposition at the end of a sentence:.I turned the TV on.If you removed 'on' from the end of this sentence, it would change the meaning. Instead of switching on the set, you would be saying that you turned the TV itself. Alternatively, this could be written as, 'I turned on the TV.' Never Substitute 'Have' for 'Of'Teachers, writers, and grammarians would cringe at this construct:. I should of come over.Eek. Although it sounds like we say this all the time; we don't really.
We might say, 'I should've come over,' but that's about it. Here's what the above sentence should look like:.
I should have come over.' Have' is an important helping verb.
The preposition 'of' does nothing here to link or join ideas together, as every preposition should. Don't Confuse 'In' and 'Into'When you want to express motion toward something, use 'into' rather than 'in.' Reserve 'in' for moments when you want to indicate a location. Here are some examples:. I swam in the lake. (Indicating location).
I walked into the pub. (Expressing motion). Look in the cupboard. (Indicating location). She drove into the city.
(Expressing motion)6. Try Not to Interchange 'Than' and 'From'We'll close with more of a suggestion than a hard and fast rule. It deals with the word 'different.' Try to avoid this:.
You look different than your mother.Instead, opt for:. You look different from your mother.

:::: Rules🤣Six Preposition RulesPrepositions form a small but very important word class. We use prepositions very frequently used. In fact, the prepositions to, of, in, for, on, with, at, by, from are all in the top 25 words in English.
If you can understand and correctly use prepositions, it will greatly improve your fluency. And remember, there are not very many prepositions.
There are only and we only use commonly. The following rules will help you understand and use prepositions correctly. A preposition must have an objectAll prepositions have objects. If a 'preposition' does not have an object it is not a preposition—it's probably an adverb. A preposition always has an object. An adverb never has an object. Look at these example sentences:.
They are in the kitchen. (preposition in has object the kitchen)Please come in. (adverb in has no object; it qualifies come). There was a doorway before me. (preposition before has object me)I had never seen it before. (adverb before has no object; it qualifies seen). I will call after work. (preposition after has object work)He called soon after. (adverb after has no object; it qualifies called)2.
Pre-position means place beforeThe name “ preposition” indicates that a preposition (usually) comes before something (its object):. I put it in the box.But even when a preposition does not come before its object, it is still closely related to its object:. Who did you talk to?
/ I talked to Jane.3. A pronoun following a preposition should be in object formThe noun or pronoun that follows a preposition forms a ‘prepositional object’. If it is a pronoun, it should therefore be in the objective form ( me, her, them), not subjective form ( I, she, they):. This is from my wife and me. That’s between him and her.
Mary gave it to them.4. Preposition formsPrepositions have no particular form. The majority of prepositions are one-word prepositions, but some are two- or three-word phrases known as complex-prepositions:. one-word prepositions (before, into, on).
complex prepositions (according to, but for, in spite of, on account of)5. To preposition and to infinitive are not the sameDo not confuse the infinitive particle “to” ( to sing, to live) with the preposition “to” ( to London, to me).to as preposition.
I look forward to lunchI look forward to seeing youI look forward to see you. They are committed to the project.They are committed to keeping the price down.They are committed to keep the price down. I am used to cars.I am used to driving.I am used to drive.to as infinitive particle. They used to live in Moscow.
They love to sing.6. The golden preposition ruleA preposition is followed by a 'noun'. It is NEVER followed by a verb.Read more about.
For a full list of prepositions plus examples and quizzes, you may like this PDF ebook, by EnglishClub founder Josef Essberger. 94 one-word prepositions and 56 complex prepositions. 400 example sentences. 200 quiz questions, with answers. illustrated. immediate download to your computer. read on your computer or print out on paper.
runs on Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS and Android:::: Rules.
